
Radiological Anatomy Sylvian Fissure Stepwards
The human cortex is several centimetres thick and has a surface area of about 2,000 square cm (310 square inches), largely because of an elaborate series of convolutions; the extensive development of this cortex in humans is thought to distinguish the human brain from those of other animals.

Photograph Transverse Section of the Brain Science Source Images
transverse fissure anatomy Learn about this topic in these articles: cerebral fissures In cerebrum.parietal and occipital lobes; the transverse fissure, which divides the cerebrum from the cerebellum; and the longitudinal fissure, which divides the cerebrum into two hemispheres. Home Health & Medicine Anatomy & Physiology Science & Tech brain

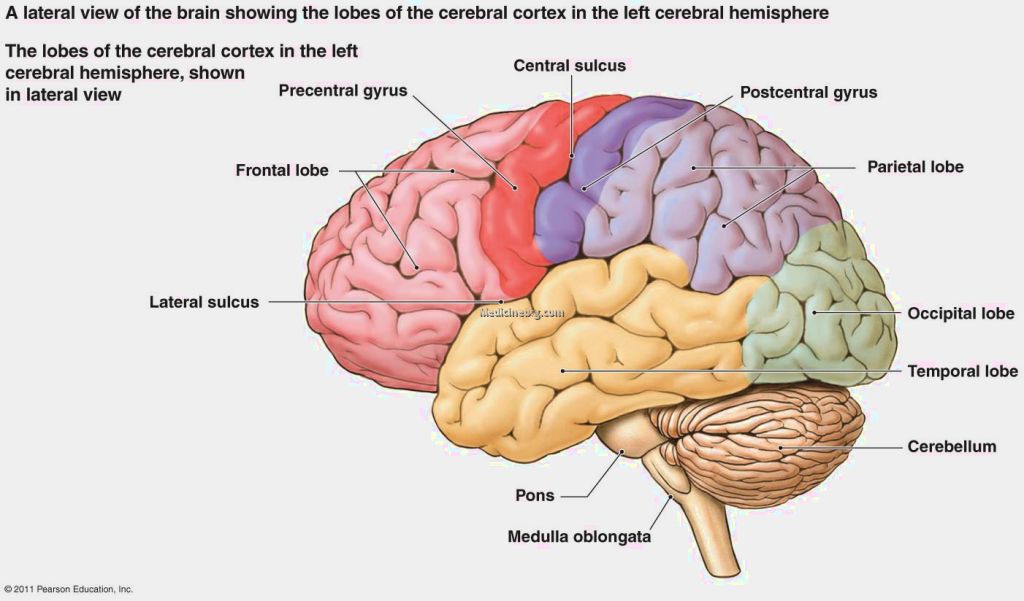
Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres. Occipital lobe, Arteries and veins
Normally, the brain is surrounded by a special tough cover called "dura mater", or simply dura. When a fistula forms between an artery and a vein within the dura, it is called Brain Dural Fistula, or Brain Dural Arteriovenous Fistula, or BDAVF, etc. When a fistula forms, blood from an artery under high pressure and flow goes directly into a.
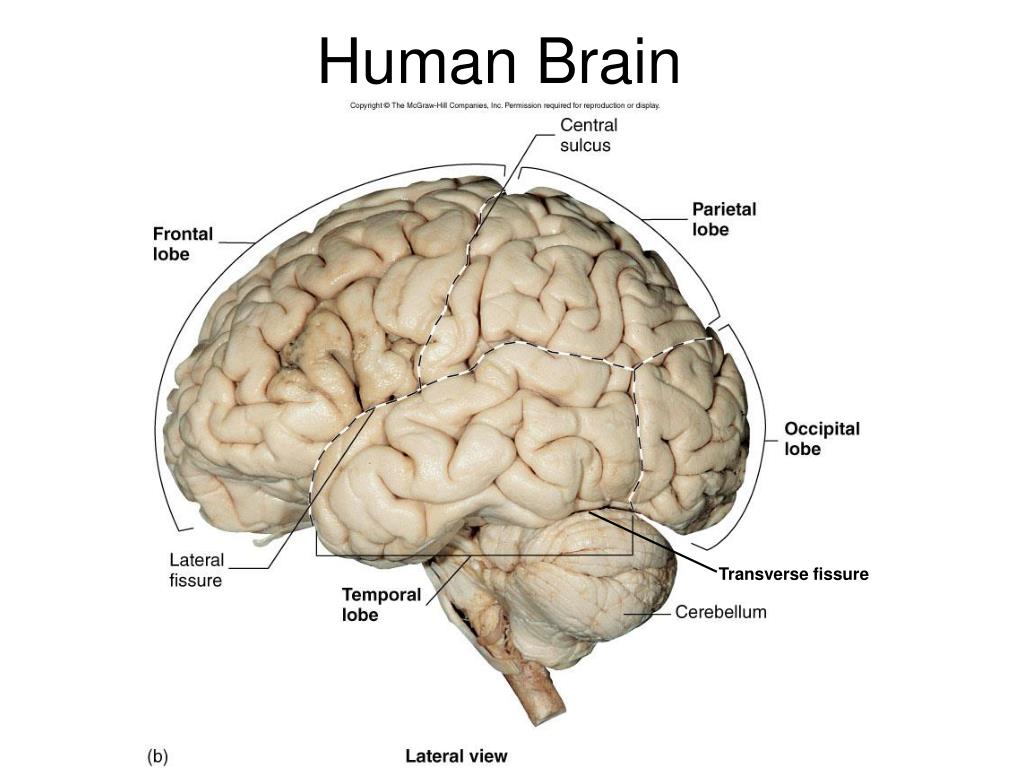
PPT LABORATORY EIGHT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID297908
Figure 11.7.5 11.7. 5: These two figures show the fissures located on the surface of the brain with the longitudinal fissure on the left and the transverse fissure on the right. 6. If you flip the brain over to the other side, you can see the cerebellum, it will be loosely attached to the cerebrum in most cases.
PPT Chapter 14 The Central Nervous System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID292396
The sylvian fissure (SyF) is the most prominent and complex fissure of the brain, promptly identifiable at the superolateral face of the brain, and harbors its underlying Sylvian cistern (SyC). Since 1976, Yasargil et al. [ 1] emphasized the importance of the SyF, describing in detail its microanatomy and related surgical approaches, to.
Fissures Of The Brain
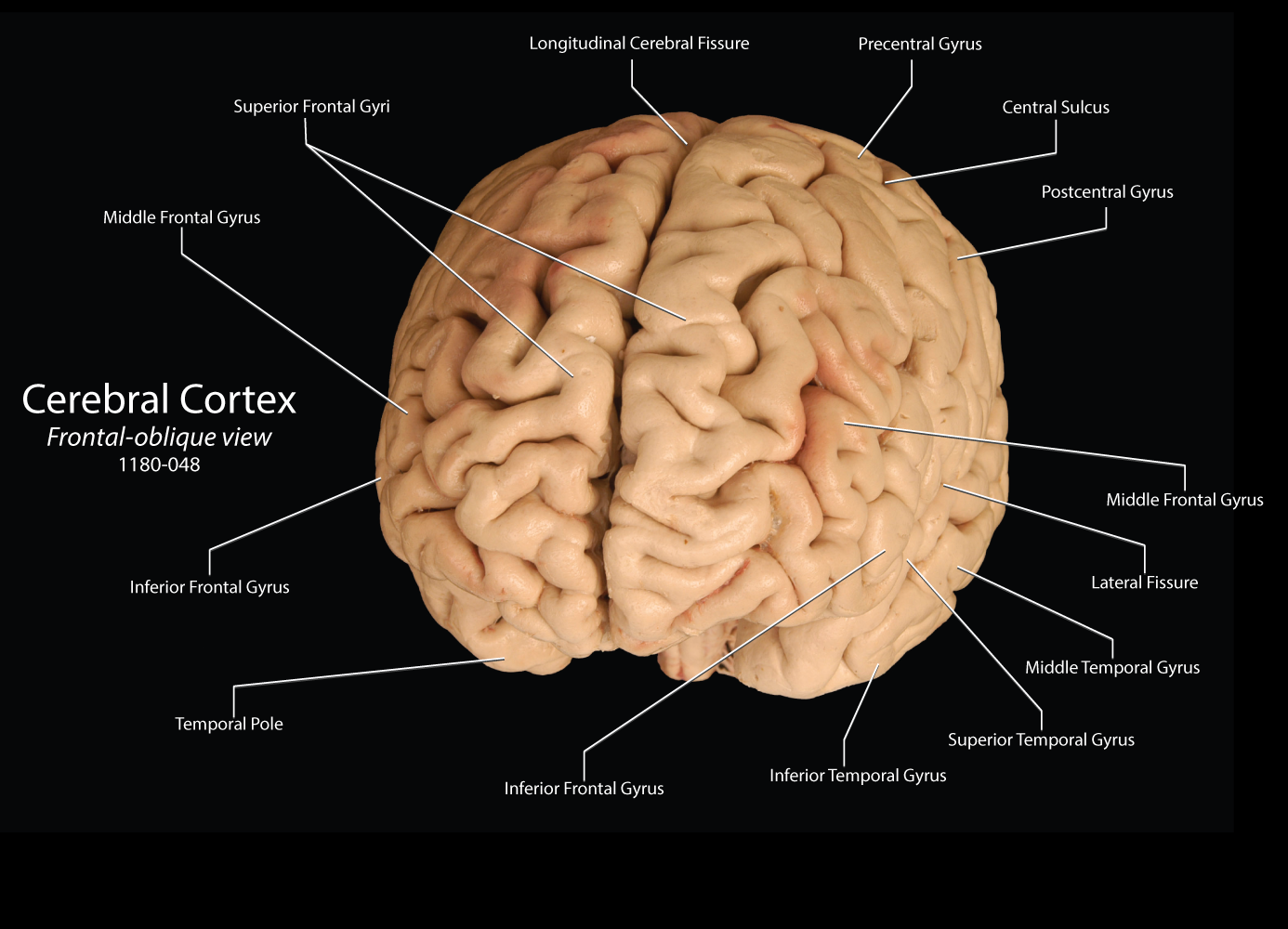
A gyrus (plural: gyri) is a ridge on the surface of the brain. Each ridge is surrounded by fissures known as sulci (singular: sulcus). Gyri are unique structures that have an important evolutionary function; they increase the surface area of the brain up to an impressive 2000 centimeters squared.

Major Fissures Of The Brain BRAINLYZF
Transverse fissure of liver, found in the lower surface of the liver Umbilical fissure, found in front of the liver Lung Azygos fissure, of right lung Horizontal fissure of right lung Oblique fissure, of the right and left lungs Skull Auricular fissure, found in the temporal bone Petrotympanic fissure Pterygomaxillary fissure
What Is The Longitudinal Fissure Of The Brain
The transverse cerebral fissure (cerebral fissure of Bichat) is a fissure between the corpus callosum and the fornix above the thalamus and the roof of the third ventricle below. Text by Antoine Micheau, MD - Copyright IMAIOS

Fissures Of The Brain
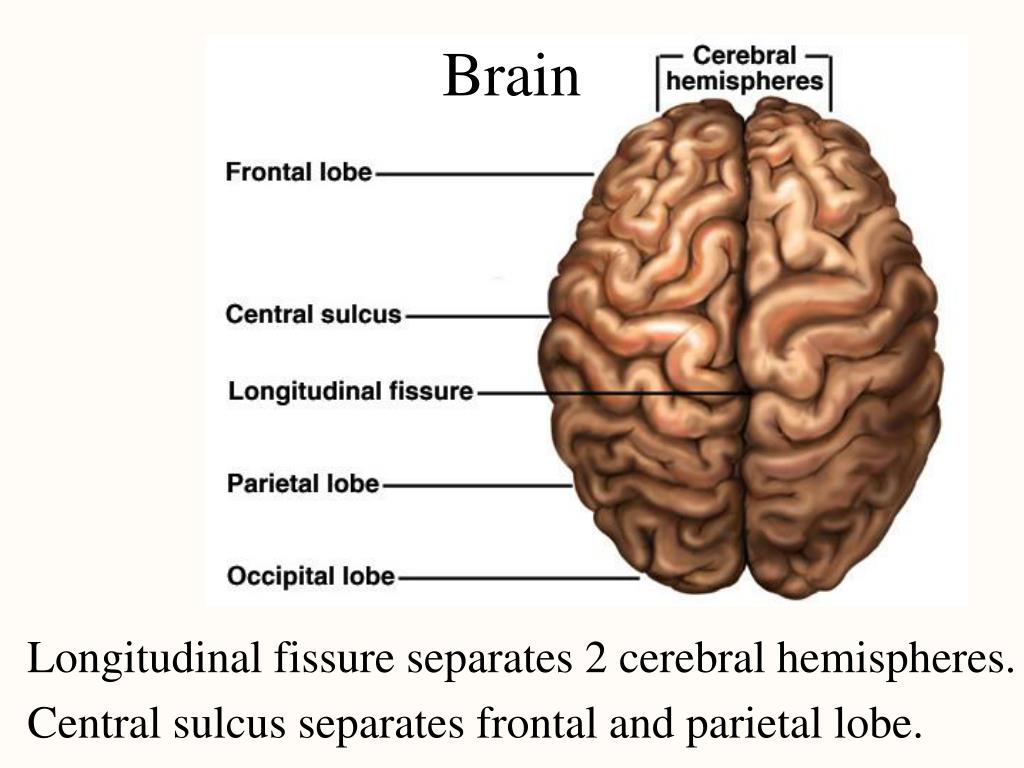
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater (one of the meninges) called the falx cerebri. [1]
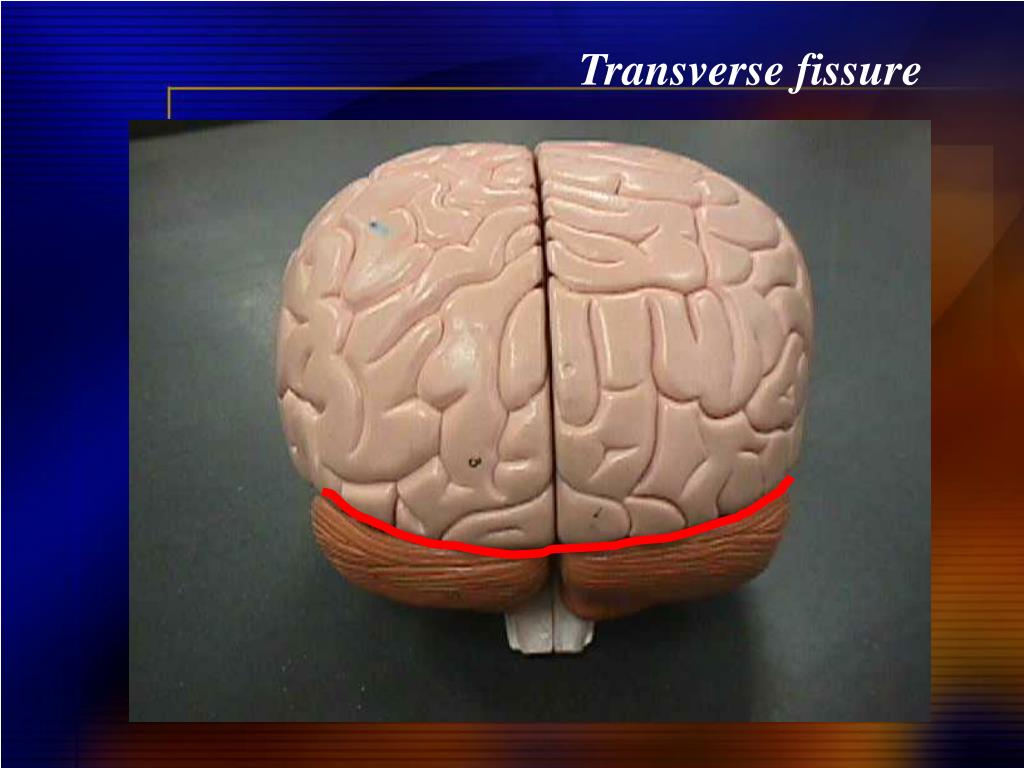
PPT Lab Ex. 28 Brain & Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1162432
Go to: Structure and Function The surface of the cerebrum is known as the cortex. It is about two-millimeter-thick and has many folds forming ridges (gyri) and grooves (sulci). A fissure is a deeper grove and is often used interchangeably with sulcus.

Transverse Brain Section through Upper Thalamus Diagram Quizlet
A fissure or groove that separates the two hemispheres is called the great longitudinal fissure. The two sides of the brain are joined at the bottom by the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum connects the two halves of the brain and delivers messages from one half of the brain to the other. The surface of the cerebrum contains billions of.

PPT Brain Topography PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3065672
In control brains, the lateral part of the transverse fissure is a narrow cleft protruding laterally as choroid and hippocampal recesses. In AD-affected brains, the lateral part of the transverse fissure becomes a large subarachnoid space as a result of different degrees of atrophy of various hippocampal and parahippocampal structures.

A transverse crosssection of the brain in the area of the optic... Download Scientific Diagram
Underneath the brain, the frontal and temporal lobes are visible, as is the cerebellum. Like the dorsal view, the longitudinal fissure divides the cerebrum into right and left hemispheres. The pons and medulla (components of the brain stem) connect the cerebrum to the spinal cord. Fig 23.9. Ventral Surface of the Brain.

Neuromuscular The Rehabilitation Specialist's Handbook, 4e F.A. Davis PT Collection McGraw
The transverse fissure (of Bichat) is the cerebral fissure that extends laterally from the ambient cistern towards the hippocampus. Gross anatomy The transverse fissure is the lateral extension of the ambient cistern that connects with the choroidal fissure superolaterally and hippocampal fissure inferolaterally.

Lab 4 Brain Deep Fissures Diagram Quizlet
Cross sectional anatomy: MRI of the brain. An MRI was performed on a healthy subject, with several acquisitions with different weightings: spin-echo T1, T2 and FLAIR, T2 gradient-echo, diffusion, and T1 after gadolinium injection. We obtained 24 axial slices of the normal brain. Data and DICOM images archived on our PACS (Picture Archiving and.
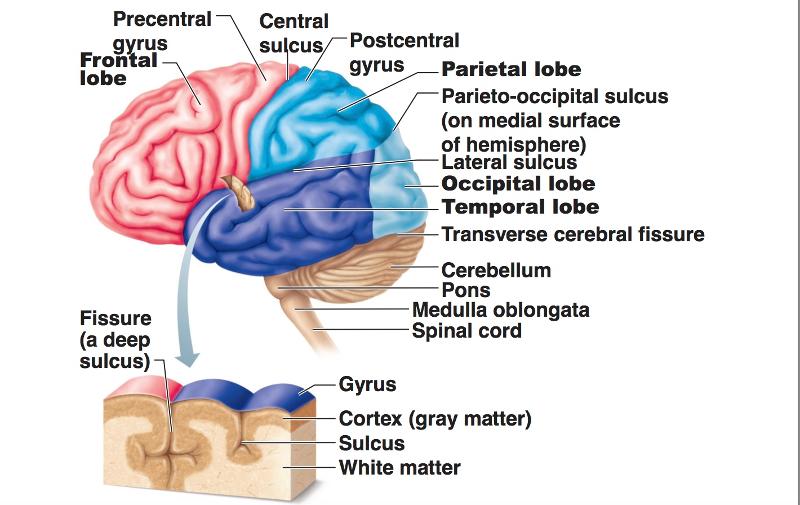
Chapter 12 The CNS (Brain and Spinal Cord) Flashcards Easy Notecards
Exercise 1: Utilize the model of the human brain to locate the following structures / landmarks for the cerebrum: Longitudinal fissure Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Central sulcus Precentral gyrus DIENCEPHALON: Postcentral gyrus Occipital lobe Parieto-occipital sulcus Temporal lobe Lateral sulcus Transverse fissure